How Does WhatsApp Make Money? [2025 Business Model Revealed]
One of the most widely used messaging apps is WhatsApp, which has over 2 billion users worldwide. It’s fast, encrypted, and completely free—so the million-dollar question is: how does WhatsApp make money?
While many users believe WhatsApp doesn’t earn much due to the absence of ads or direct charges, the reality is far more strategic. This article unpacks WhatsApp’s revenue streams, including the WhatsApp Business API, Meta’s data ecosystem, and what the future holds for monetization.
Let’s dive into how a “free” app is turning into a multi-billion-dollar business.
Understanding WhatsApp’s Business Strategy
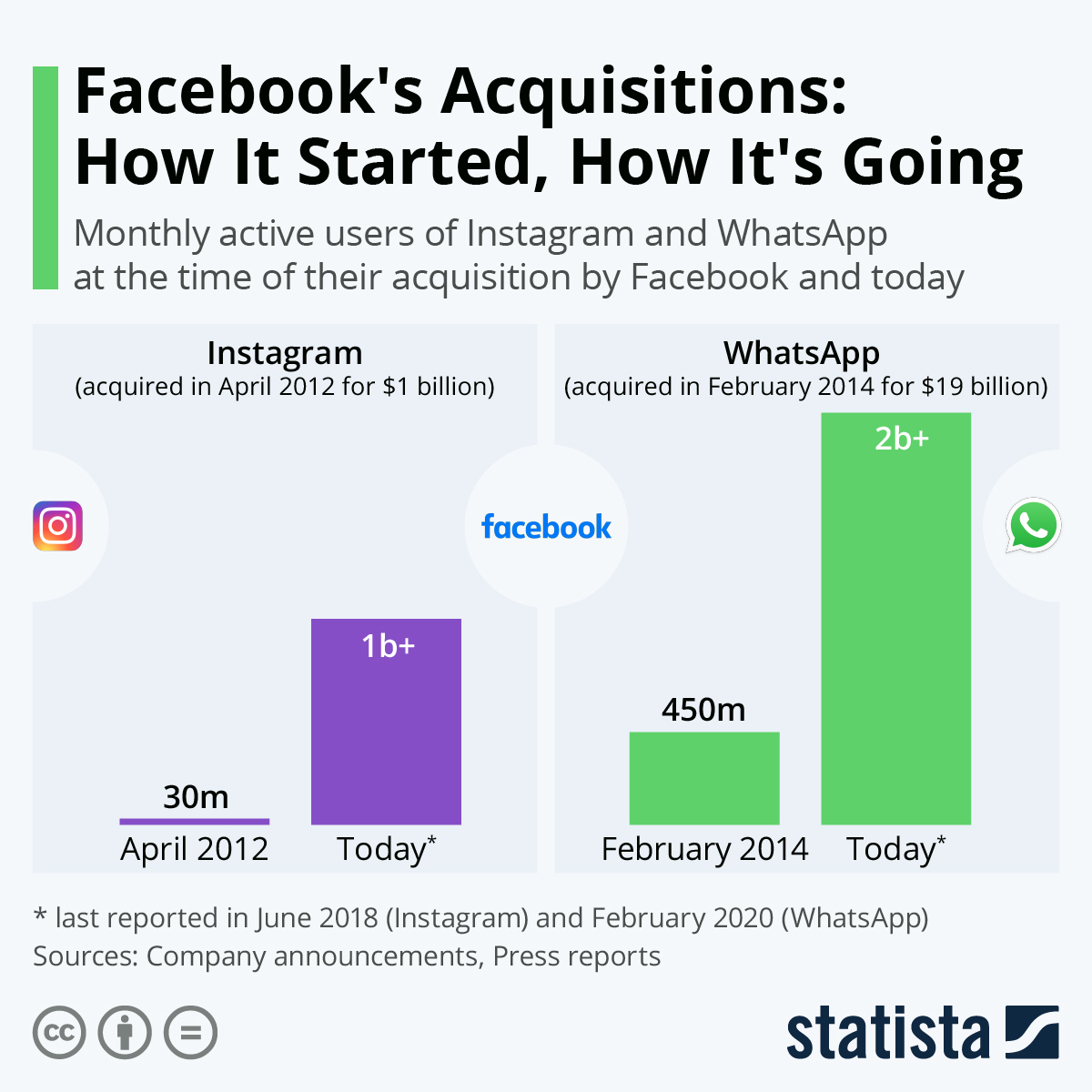
Former Yahoo engineers Jan Koum and Brian Acton founded WhatsApp in 2009.In 2014, Facebook (now Meta) acquired WhatsApp for a staggering $19 billion—one of the largest tech acquisitions ever.
Back then, WhatsApp followed a simple model: $1 annual subscription. But after the Meta acquisition, that fee was removed, and the app became free for everyone.
So, why would Meta buy and maintain a free app?
Because Meta isn’t playing for small gains. WhatsApp fits into a broader strategy that revolves around ecosystem control, user engagement, and long-term monetization through business services and data integration.
You will find more infographics at Statista
Is WhatsApp Really Free?
Yes, WhatsApp is free for users, but that doesn’t mean it’s a charity service.
Let’s clear up a few common misconceptions:
- Do you have to pay for WhatsApp?
No, downloading and using the app is free.
- Does WhatsApp charge for messages or calls?
No, internet data is used for all communication.
Then how does WhatsApp support its infrastructure? The answer lies in business users and enterprise tools, not the average user.
Read more: WhatsApp official FAQ on charges
Does WhatsApp Charge for International Calls?
No. Whether you’re in the U.S. or Pakistan, WhatsApp doesn’t charge you directly for calls—even international ones.
Instead, WhatsApp uses VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol) to transmit calls over the internet. You’re using mobile data or Wi-Fi, not a traditional mobile network.
However, your data carrier may charge you for data usage, especially when roaming. This raises a secondary revenue topic: indirect monetization via partnerships and internet consumption.
Main Revenue Source – WhatsApp Business API
Now we get to the heart of WhatsApp’s revenue engine: the WhatsApp Business API.
Launched in 2018, the API is designed for medium and large businesses to communicate with customers at scale. No, internet data is used for all communication. The API is not free, in contrast to the free WhatsApp Business app. Businesses are billed by Meta using a conversation-based pricing model.
Key Features:
- Automated messaging with chatbots
- CRM integration
- Verified business profiles
- Priority customer support tools
Real-Life Example: Airlines like KLM and brands like Unilever use the WhatsApp API for customer service and alerts.
Meta monetizes each interaction, especially customer-initiated or business-initiated messages beyond a certain threshold.
Read our guide on How WhatsApp Business Works for Small Brands
Examples of WhatsApp Business API Use
Company | Use Case | Region |
KLM Airlines | Booking confirmations & delays | Europe |
Flipkart | Order updates & delivery alerts | India |
Jumia | Promotions & support chatbots | Africa |
Bank of America | Account alerts & authentication | USA |
Source: Google Cloud’s State of APIs 2025
Does WhatsApp Sell User Data?
Here’s where things get sensitive. While WhatsApp uses end-to-end encryption, Meta does collect metadata—information about the communication, not the messages themselves.
- What WhatsApp shares with Meta:
- Your phone number
- Device and location information
- How often you use the app
- With whom you communicate (not the message content)
This data helps Meta improve ad targeting on Facebook and Instagram—an indirect way WhatsApp contributes to Meta’s revenue.
What Data is Shared with Meta?
Shared Data | Used For |
Phone number | Account linking across platforms |
Usage frequency | Targeted advertising on Meta products |
Device info | Platform performance optimization |
Meta does not sell your data, but it integrates user behavior across platforms to enhance ad targeting.
How WhatsApp Benefits Facebook Financially
Let’s connect the dots.
WhatsApp itself doesn’t run ads. But your usage data and identity are linked to Meta’s advertising system. The more people spend time on WhatsApp, the more data Meta can use to deliver precise ads on Facebook, Messenger, and Instagram.
This cross-platform integration is extremely valuable for:
- Advertisers who want pinpoint targeting
- With lower customer acquisition expenses, Meta will increase its ad revenue.
Future Revenue Streams for WhatsApp
Meta isn’t stopping at messaging. It’s exploring several future revenue channels:
- WhatsApp Pay (peer-to-peer transfers)
- In-app services (food ordering, bookings)
- Ads in business messages (pilot testing underway)
- Premium WhatsApp Business subscriptions (custom catalogs, links)
According to reports, India and Brazil are key markets for WhatsApp Pay, with millions of active users already.
WhatsApp Pay and In-App Purchases
WhatsApp Pay operates like a simplified Venmo or Google Pay—users can send and receive money instantly. Meta plans to earn via:
- Merchant fees
- In-app commerce tools
- Branded storefronts
Read more: Learn more about How WhatsApp Pay is Changing Mobile Payments
Key Differences Between WhatsApp Personal & Business
H2: Is WhatsApp Really Free?
Yes, WhatsApp is free for users, but that doesn’t mean it’s a charity service.
Let’s clear up a few common misconceptions:
- Do you have to pay for WhatsApp?
No, downloading and using the app is free.
- Does WhatsApp charge for messages or calls?
No, internet data is used for all communication.
Then how does WhatsApp support its infrastructure? The answer lies in business users and enterprise tools, not the average user.
External Link Suggestion: WhatsApp official FAQ on charges
Does WhatsApp Charge for International Calls?
No. Whether you’re in the U.S. or Pakistan, WhatsApp doesn’t charge you directly for calls—even international ones.
Instead, WhatsApp uses VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol) to transmit calls over the internet. You’re using mobile data or Wi-Fi, not a traditional mobile network.
However, your data carrier may charge you for data usage, especially when roaming. This raises a secondary revenue topic: indirect monetization via partnerships and internet consumption.
Main Revenue Source – WhatsApp Business API
Now we get to the heart of WhatsApp’s revenue engine: the WhatsApp Business API.
Launched in 2018, the API is designed for medium and large businesses to communicate with customers at scale. No, internet data is used for all communication. The API is not free, in contrast to the free WhatsApp Business app. Businesses are billed by Meta using a conversation-based pricing model.
Key Features:
- Automated messaging with chatbots
- CRM integration
- Verified business profiles
- Priority customer support tools
Real-Life Example: Airlines like KLM and brands like Unilever use the WhatsApp API for customer service and alerts.
Meta monetizes each interaction, especially customer-initiated or business-initiated messages beyond a certain threshold.
Internal Link Suggestion: Read our guide on How WhatsApp Business Works for Small Brands
Examples of WhatsApp Business API Use
Company | Use Case | Region |
KLM Airlines | Booking confirmations & delays | Europe |
Flipkart | Order updates & delivery alerts | India |
Jumia | Promotions & support chatbots | Africa |
Bank of America | Account alerts & authentication | USA |
Does WhatsApp Sell User Data?
Here’s where things get sensitive. While WhatsApp uses end-to-end encryption, Meta does collect metadata—information about the communication, not the messages themselves.
- What WhatsApp shares with Meta:
- Your phone number
- Device and location information
- How often you use the app
- With whom you communicate (not the message content)
This data helps Meta improve ad targeting on Facebook and Instagram—an indirect way WhatsApp contributes to Meta’s revenue.
What Data is Shared with Meta?
Shared Data | Used For |
Phone number | Account linking across platforms |
Usage frequency | Targeted advertising on Meta products |
Device info | Platform performance optimization |
Meta does not sell your data, but it integrates user behavior across platforms to enhance ad targeting.
How WhatsApp Benefits Facebook Financially
Let’s connect the dots.
WhatsApp itself doesn’t run ads. But your usage data and identity are linked to Meta’s advertising system. The more people spend time on WhatsApp, the more data Meta can use to deliver precise ads on Facebook, Messenger, and Instagram.
This cross-platform integration is extremely valuable for:
- Advertisers who want pinpoint targeting
- With lower customer acquisition expenses, Meta will increase its ad revenue.

Future Revenue Streams for WhatsApp
Meta isn’t stopping at messaging. It’s exploring several future revenue channels:
- WhatsApp Pay (peer-to-peer transfers)
- In-app services (food ordering, bookings)
- Ads in business messages (pilot testing underway)
- Premium WhatsApp Business subscriptions (custom catalogs, links)
According to reports, India and Brazil are key markets for WhatsApp Pay, with millions of active users already.
WhatsApp Pay and In-App Purchases
WhatsApp Pay operates like a simplified Venmo or Google Pay—users can send and receive money instantly. Meta plans to earn via:
- Merchant fees
- In-app commerce tools
- Branded storefronts
Learn more about How WhatsApp Pay is Changing Mobile Payments
Key Differences Between WhatsApp Personal & Business
Feature | WhatsApp Business | WhatsApp Business API | |
End-to-End Encryption | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
Automated Replies | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ |
API Access | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ |
Monthly Charges | ❌ | ❌ | ✅(tier-based) |
Catalogs & Labels | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ |
Large-Scale Messaging | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ |
Summary of WhatsApp’s Monetization Model
Revenue Channel | Description |
WhatsApp Business API | Charged per conversation; major income source |
Indirect Meta Ad Revenue | Metadata enhances ad targeting on Meta platforms |
WhatsApp Pay (Emerging) | Future revenue via merchant tools |
Premium Business Tools | Potential subscriptions in development |
Suggested Reading: WhatsApp Business vs Telegram Business
Interested in how WhatsApp compares with its rivals? Read our detailed guide on how Telegram, Signal, and WhatsApp stack up for businesses.
Click here to read
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Do I have to pay for WhatsApp?
How does WhatsApp make money if it’s free?
Does WhatsApp use or sell my data?
What is the WhatsApp Business API?
Can I use WhatsApp for international calls for free?
Is WhatsApp planning to show ads?
Final Thoughts: Is WhatsApp’s Free Model Sustainable?
WhatsApp’s monetization strategy reflects a modern shift in tech—the product is free, but the service is not. By monetizing businesses, integrating with Meta’s ad systems, and expanding into payments, WhatsApp has built a sustainable revenue model without compromising the user experience.
The app will likely remain free for personal users. But behind the scenes, it’s becoming a key profit engine for Meta.